Coming Up ACEs: Decoding the AI Technology That’s Enhancing Games With Realistic Digital Humans
Editor’s note: This post is part of the AI Decoded series, which demystifies AI by making the technology more accessible, and which showcases new hardware, software, tools and accelerations for RTX PC users.
Digital characters are leveling up.
Non-playable characters often play a crucial role in video game storytelling, but since they’re usually designed with a fixed purpose, they can get repetitive and boring — especially in vast worlds where there are thousands.
Thanks in part to incredible advances in visual computing like ray tracing and DLSS, video games are more immersive and realistic than ever, making dry encounters with NPCs especially jarring.
Earlier this year, production microservices for the NVIDIA Avatar Cloud Engine launched, giving game developers and digital creators an ace up their sleeve when it comes to making lifelike NPCs. ACE microservices allow developers to integrate state-of-the-art generative AI models into digital avatars in games and applications. With ACE microservices, NPCs can dynamically interact and converse with players in-game and in real time.
Leading game developers, studios and startups are already incorporating ACE into their titles, bringing new levels of personality and engagement to NPCs and digital humans.
Bring Avatars to Life With NVIDIA ACE
The process of creating NPCs starts with providing them a backstory and purpose, which helps guide the narrative and ensures contextually relevant dialogue. Then, ACE subcomponents work together to build avatar interactivity and enhance responsiveness.
NPCs tap up to four AI models to hear, process, generate dialogue and respond.
The player’s voice first goes into NVIDIA Riva, a technology that builds fully customizable, real-time conversational AI pipelines and turns chatbots into engaging and expressive assistants using GPU-accelerated multilingual speech and translation microservices.
With ACE, Riva’s automatic speech recognition (ASR) feature processes what was said and uses AI to deliver a highly accurate transcription in real time. Explore a Riva-powered demo of speech-to-text in a dozen languages.
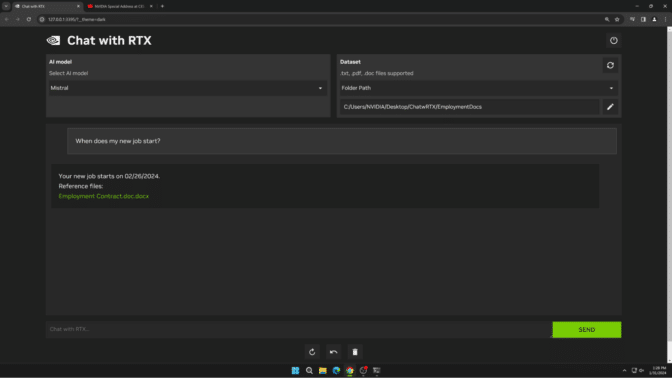
The transcription then goes into an LLM — such as Google’s Gemma, Meta’s Llama 2 or Mistral — and taps Riva’s neural machine translation to generate a natural language text response. Next, Riva’s Text-to-Speech functionality generates an audio response.
Finally, NVIDIA Audio2Face (A2F) generates facial expressions that can be synced to dialogue in many languages. With the microservice, digital avatars can display dynamic, realistic emotions streamed live or baked in during post-processing.
The AI network automatically animates face, eyes, mouth, tongue and head motions to match the selected emotional range and level of intensity. And A2F can automatically infer emotion directly from an audio clip.
Each step happens in real time to ensure fluid dialogue between the player and the character. And the tools are customizable, giving developers the flexibility to build the types of characters they need for immersive storytelling or worldbuilding.
Born to Roll
At GDC and GTC, developers and platform partners showcased demos leveraging NVIDIA ACE microservices — from interactive NPCs in gaming to powerful digital human nurses.
Ubisoft is exploring new types of interactive gameplay with dynamic NPCs. NEO NPCs, the product of its latest research and development project, are designed to interact in real time with players, their environment and other characters, opening up new possibilities for dynamic and emergent storytelling.
The capabilities of these NEO NPCs were showcased through demos, each focused on different aspects of NPC behaviors, including environmental and contextual awareness; real-time reactions and animations; and conversation memory, collaboration and strategic decision-making. Combined, the demos spotlighted the technology’s potential to push the boundaries of game design and immersion.
Using Inworld AI technology, Ubisoft’s narrative team created two NEO NPCs, Bloom and Iron, each with their own background story, knowledge base and unique conversational style. Inworld technology also provided the NEO NPCs with intrinsic knowledge of their surroundings, as well as interactive responses powered by Inworld’s LLM. NVIDIA A2F provided facial animations and lip syncing for the two NPCs real time.
Inworld and NVIDIA set GDC abuzz with a new technology demo called Covert Protocol, which showcased NVIDIA ACE technologies and the Inworld Engine. In the demo, players controlled a private detective who completed objectives based on the outcome of conversations with NPCs on the scene. Covert Protocol unlocked social simulation game mechanics with AI-powered digital characters that acted as bearers of crucial information, presented challenges and catalyzed key narrative developments. This enhanced level of AI-driven interactivity and player agency is set to open up new possibilities for emergent, player-specific gameplay.
Built on Unreal Engine 5, Covert Protocol uses the Inworld Engine and NVIDIA ACE, including NVIDIA Riva ASR and A2F, to augment Inworld’s speech and animation pipelines.
In the latest version of the NVIDIA Kairos tech demo built in collaboration with Convai, which was shown at CES, Riva ASR and A2F were used to significantly improve NPC interactivity. Convai’s new framework allowed the NPCs to converse among themselves and gave them awareness of objects, enabling them to pick up and deliver items to desired areas. Furthermore, NPCs gained the ability to lead players to objectives and traverse worlds.
Digital Characters in the Real World
The technology used to create NPCs is also being used to animate avatars and digital humans. Going beyond gaming, task-specific generative AI is moving into healthcare, customer service and more.
NVIDIA collaborated with Hippocratic AI at GTC to extend its healthcare agent solution, showcasing the potential of a generative AI healthcare agent avatar. More work underway to develop a super-low-latency inference platform to power real-time use cases.
“Our digital assistants provide helpful, timely and accurate information to patients worldwide,” said Munjal Shah, cofounder and CEO of Hippocratic AI. “NVIDIA ACE technologies bring them to life with cutting-edge visuals and realistic animations that help better connect to patients.”
Internal testing of Hippocratic’s initial AI healthcare agents is focused on chronic care management, wellness coaching, health risk assessments, social determinants of health surveys, pre-operative outreach and post-discharge follow-up.
UneeQ is an autonomous digital human platform focused on AI-powered avatars for customer service and interactive applications. UneeQ integrated the NVIDIA A2F microservice into its platform and combined it with its Synanim ML synthetic animation technology to create highly realistic avatars for enhanced customer experiences and engagement.
“UneeQ combines NVIDIA animation AI with our own Synanim ML synthetic animation technology to deliver real-time digital human interactions that are emotionally responsive and deliver dynamic experiences powered by conversational AI,” said Danny Tomsett, founder and CEO at UneeQ.
AI in Gaming
ACE is one of the many NVIDIA AI technologies that bring games to the next level.
- NVIDIA DLSS is a breakthrough graphics technology that uses AI to increase frame rates and improve image quality on GeForce RTX GPUs.
- NVIDIA RTX Remix enables modders to easily capture game assets, automatically enhance materials with generative AI tools and quickly create stunning RTX remasters with full ray tracing and DLSS.
- NVIDIA Freestyle, accessed through the new NVIDIA app beta, lets users personalize the visual aesthetics of more than 1,200 games through real-time post-processing filters, with features like RTX HDR, RTX Dynamic Vibrance and more.
- The NVIDIA Broadcast app transforms any room into a home studio, giving livestream AI-enhanced voice and video tools, including noise and echo removal, virtual background and AI green screen, auto-frame, video noise removal and eye contact.
Experience the latest and greatest in AI-powered experiences with NVIDIA RTX PCs and workstations, and make sense of what’s new, and what’s next, with AI Decoded.
Get weekly updates directly in your inbox by subscribing to the AI Decoded newsletter.