The 9/11 Plotters Should Have Been Found Guilty in a Real Court
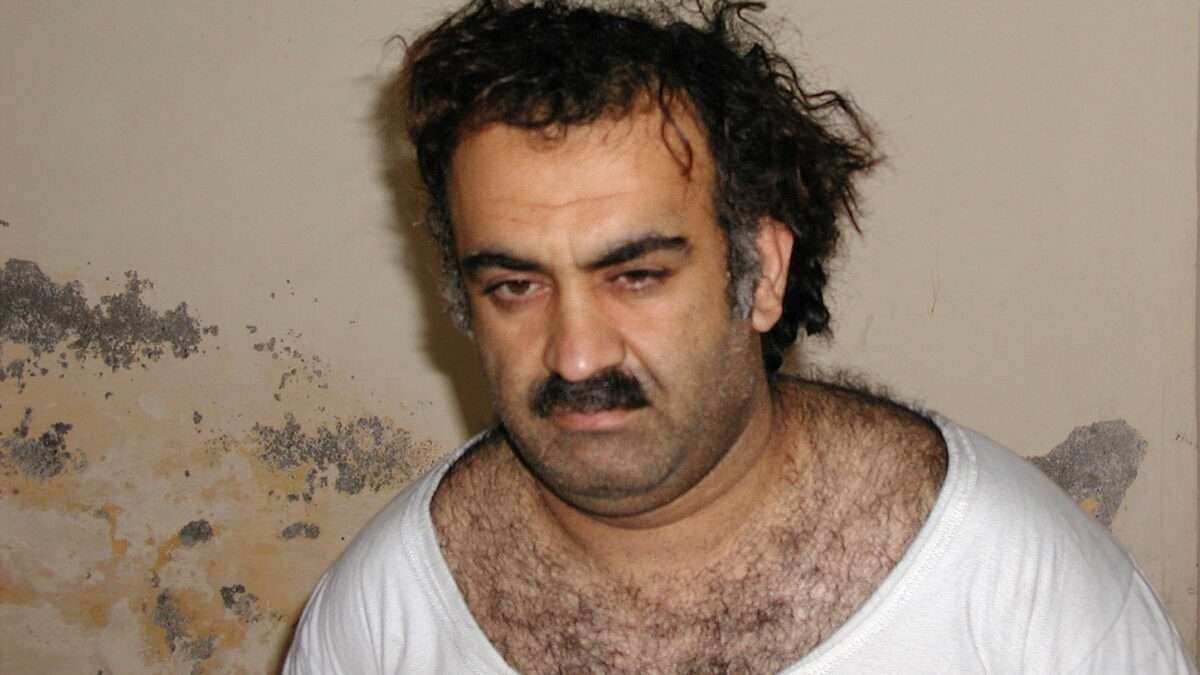
Khalid Sheikh Mohammed and two other Al Qaeda members behind the 9/11 attacks pleaded guilty to 2,976 counts of murder, U.S. military prosecutors revealed in a letter to 9/11 victim families on Wednesday. In exchange, the 9/11 plotters will escape the death penalty. The letter called the plea deal "the best path to finality and justice in this case."
Mohammed and his accomplices were first taken into U.S. custody in 2003. There was little doubt of their guilt; Mohammed admitted to plotting the attacks to a TV reporter a year before his capture. So why was a plea deal in a shadowy military court more than twenty years later the best that the U.S. government could do?
It was a self-inflicted problem. Rather than letting law enforcement handle a massacre on American soil, President George W. Bush had the suspects rounded up into secretive torture prisons, forever tainting the evidence. No court would admit torture-derived confessions—and any statement made after the torture could also be challenged by lawyers. After all, several known innocents have also confessed under torture.
When the Obama administration tried to put Mohammed on trial in New York, the scene of his crime, politicians from both parties helped stir up public outrage. Congress passed a bipartisan law preventing Al Qaeda suspects from being moved to the U.S. mainland. Instead, Mohammed and other defendants were tried by a Guantanamo Bay military tribunal that delivered neither fairness and transparency nor swift justice. It was the worst of all worlds.
The relatives of many victims felt blindsided by the plea deal.
"There's a sense of betrayal amongst the 9/11 family members right now," Brett Eagleson, president of the nonprofit 9/11 Justice, told SpyTalk, a Substack focused on national security. "We weren't consulted in any way on what was going to be happening down in Guantanamo."
The 9/11 plotters' guilty plea was one of many missed opportunities for closure on the War on Terror. After killing Al Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden, the Obama administration could have declared victory and begun the process of moving on. Instead, he promised endless war.
"His death does not mark the end of our effort," President Barack Obama said in his announcement of bin Laden's death. "There is no doubt that Al Qaeda will continue to pursue attacks against us. We must—and we will—remain vigilant at home and abroad."
This "vigilance abroad" meant war against an ever-shifting alphabet soup of Islamist rebels, most of whom had nothing to do with 9/11 and some of whom didn't exist when the War on Terror began. The American public was left confused about what they were even fighting for or against. As Rep. Sara Jacobs (D–Calif.) pointed out at a hearing last year, even the list of groups that the U.S. government considers to be "Al Qaeda affiliates" is classified.
Meanwhile, the constant feeling of siege corroded American domestic politics. Counterterrorism became an excuse to militarize the police. Obama-era defenses of drone strikes were recycled into anti-immigrant conspiracy theories. Concerns about "radicalization" and "extremism" were used to push for online censorship.
"The same tools that destabilized foreign countries were bound to destabilize America," wrote journalist Spencer Ackerman in his 2020 book, Reign of Terror. "Experiencing neither peace nor victory for such a sustained period was a volatile condition for millions of people."
All the while, it was easy to forget that the people who sparked all this fear to begin with—the perpetrators of 9/11—were either dead or behind bars.
Perhaps Bush and Obama's decisions are understandable, if not excusable, because the trauma of 9/11 was still so raw. But those decisions prevented this wound from ever healing. Two decades on, the closest thing to "finality and justice" is a sad, quiet compromise.
The post The 9/11 Plotters Should Have Been Found Guilty in a Real Court appeared first on Reason.com.