The Stop Comstock Act Doesn't Go Far Enough
New legislation would repeal parts of the Comstock Act, a Victorian-era law that's being revived to attack abortion pills.
Passed in 1873, the Comstock Act was a big deal in earlier eras, sending people to prison for publishing information about birth control, critiques of marriage, and more.
The law is vague and broad, banning the mailing of any "article, matter, thing, device, or substance" that the government deems "obscene, lewd, lascivious, indecent, filthy or vile," along with anything "designed, adapted, or intended for producing abortion, or for any indecent or immoral use." Essentially, the Comstock Act weaponizes the U.S. Postal Service to give the federal government an in against things that otherwise wouldn't be its business.
"Anthony Comstock, the law's namesake and an anti-smut crusader, lobbied for and personally enforced the law as a special agent of the U.S. Postal Service," noted the Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression (FIRE) lawyer Robert Corn-Revere in a recent piece for Reason about efforts to posthumously pardon publisher D.M. Bennett. "Under the law's broad mandate, everything that Comstock considered immoral was by definition obscene and, therefore, illegal. Comstock's concept of immorality included blasphemy, sensational novels and news stories, art, and even scientific and medical texts." (You can read more about Comstock, "the prodigal censor," here.)
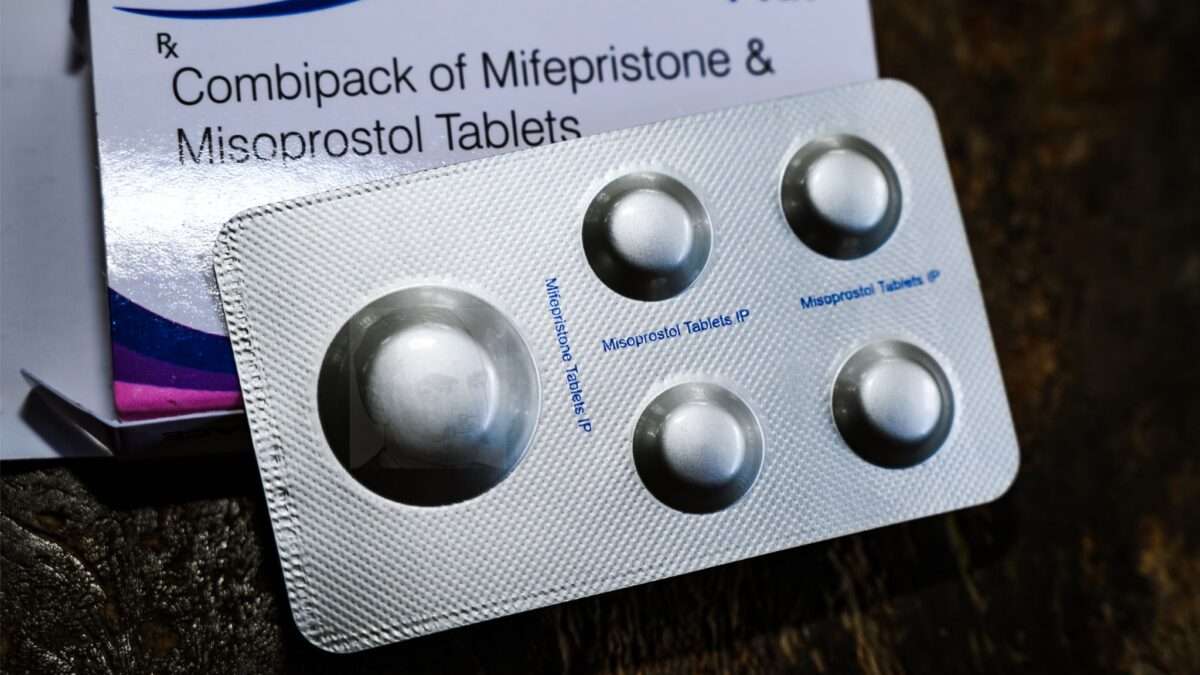
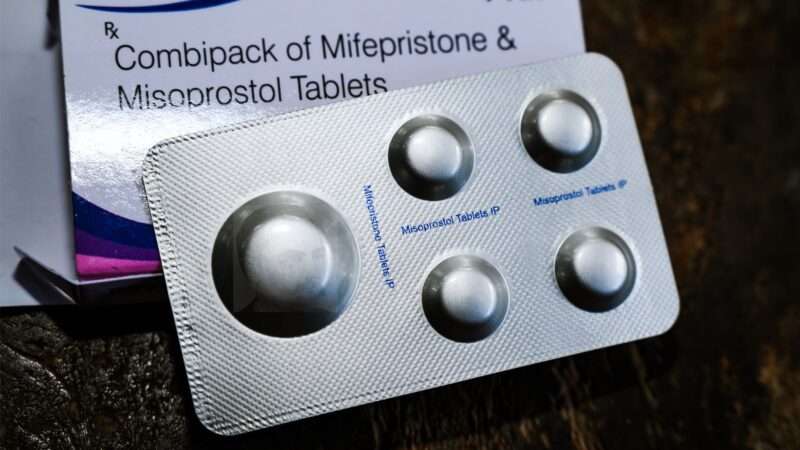
The Comstock Act lay dormant for a while, rendered toothless in part by court interpretations of the First Amendment that were more vigorously protective of free speech. But these days, activists and politicians opposed to abortion are trying to revive the law, seeing its potential usefulness in going after mifepristone and misoprostol, the two-pill regimen approved to end first-trimester pregnancies.
The resurgence of interest in the Comstock Act underscores the need to repeal bad laws, not simply assume them defanged by decades of latency.
The Biden administration certainly isn't going to start prosecuting people under the Comstock Act, but a more conservative future administration could. "[Donald] Trumps' [sic] advisors are…arguing that the Comstock Act is a de facto national abortion ban already on the books," says Madison Roberts, senior policy counsel at the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU). "They are wrong. The Department of Justice has made clear and federal appeals courts have uniformly held for almost a century that the Comstock Act does not apply to legal abortion care. But anti-abortion extremists have manipulated the law to ban abortion before, and there's no reason to think they won't try it again."
Moreover, the law was cited in a legal challenge to abortion pills and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration's decision to let them be sent via mail. The district judge who first heard the case (and sided with the plaintiffs) wrote that "dispensing of chemical abortion drugs through mail violates unambiguous federal criminal law." That case was shot down by the U.S. Supreme Court last week on procedural grounds, but it certainly won't be the last attempt to stop the prescription and mailing of abortion pills. Nor is it likely to be the last time Comstock is invoked for this purpose—unless the act is revised or repealed.
"It is too dangerous to leave this law on the books," Sen. Tina Smith (D–Minn.) said in a statement.
The Stop Comstock Act, which Smith is slated to introduce soon (no draft has been released yet, however), would repeal the parts of the law "that could be used by an anti-abortion administration to ban the mailing of mifepristone and other drugs used in medication abortions, instruments and equipment used in abortions, and educational material related to sexual health," per Smith's press release. A companion bill will be introduced in the House by Rep. Becca Balint (D–Vt.).
This is good, but not far enough, if it only partially repeals the law.
Why stop with repealing the parts that could be used to target abortion? The Comstock Act's reach is much more broad than that, and every bit could do some damage in the wrong hands.
Here's the full spate of things that the Comstock Act declares criminal to mail:
Every article or thing designed, adapted, or intended for producing abortion, or for any indecent or immoral use; and
Every article, instrument, substance, drug, medicine, or thing which is advertised or described in a manner calculated to lead another to use or apply it for producing abortion, or for any indecent or immoral purpose; and
Every written or printed card, letter, circular, book, pamphlet, advertisement, or notice of any kind giving information, directly or indirectly, where, or how, or from whom, or by what means any of such mentioned matters, articles, or things may be obtained or made, or where or by whom any act or operation of any kind for the procuring or producing of abortion will be done or performed, or how or by what means abortion may be produced, whether sealed or unsealed; and
Every paper, writing, advertisement, or representation that any article, instrument, substance, drug, medicine, or thing may, or can, be used or applied for producing abortion, or for any indecent or immoral purpose; and
Every description calculated to induce or incite a person to so use or apply any such article, instrument, substance, drug, medicine, or thing.
It's time to repeal the whole thing.
Today, it's only the abortion part of the law that people are trying to revive. But a few years ago, most of us weren't expecting a Comstock revival at all. Who's to say that a few years from now, people won't try to use it against all sorts of information, art, etc. that they don't like?
If we want to stop the Comstock Act from ever again being used to suppress speech, restrict access to contraceptives, punish people for homosexuality, and more, then we need to stop the Comstock Act entirely.
The post The Stop Comstock Act Doesn't Go Far Enough appeared first on Reason.com.