CEO of failing hospital chain got $250M amid patient deaths, layoffs, bankruptcy

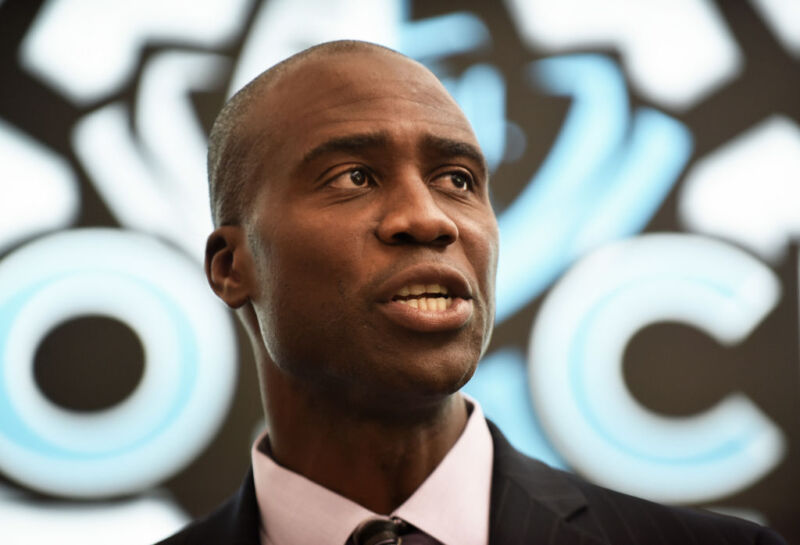
Enlarge / Hospital staff and community members held a protest in front of Carney Hospital in Boston on August 5 as Steward has announced it will close the hospital. "Ralph" refers to Steward's CEO, Ralph de la Torre, who owns a yacht. (credit: Getty | Suzanne Kreiter)
As the more than 30 hospitals in the Steward Health Care System scrounged for cash to cover supplies, shuttered pediatric and neonatal units, closed maternity wards, laid off hundreds of health care workers, and put patients in danger, the system paid out at least $250 million to its CEO and his companies, according to a report by The Wall Street Journal.
The newly revealed financial details bring yet more scrutiny to Steward CEO Ralph de la Torre, a Harvard University-trained cardiac surgeon who, in 2020, took over majority ownership of Steward from the private equity firm Cerberus. De la Torre and his companies were reportedly paid at least $250 million since that takeover. In May, Steward, which has hospitals in eight states, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy.
Critics—including members of the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions (HELP)—allege that de la Torre and stripped the system's hospitals of assets, siphoned payments from them, and loaded them with debt, all while reaping huge payouts that made him obscenely wealthy.