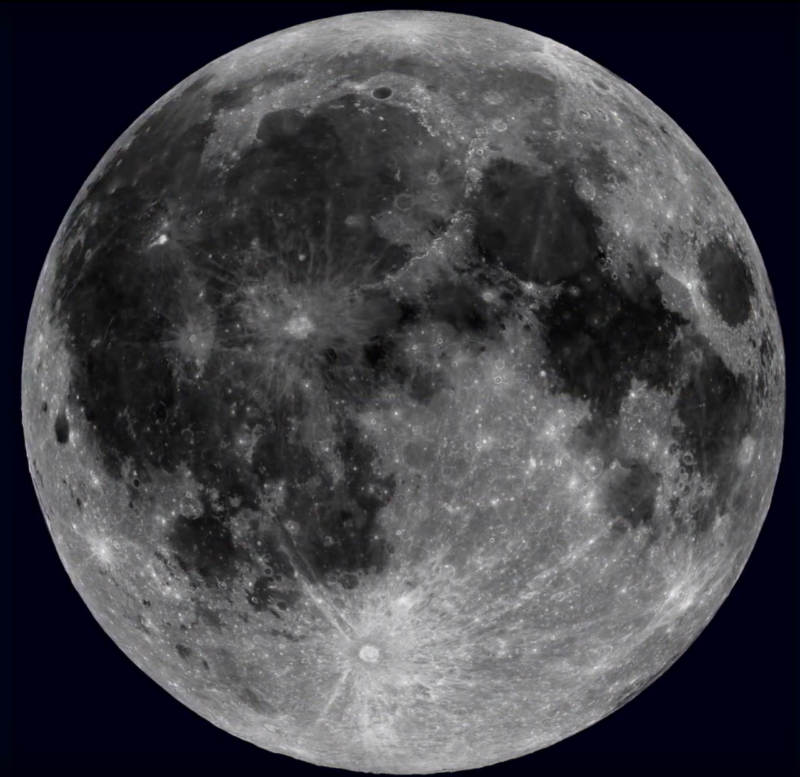
How the Moon got a makeover

Enlarge (credit: NASA Goddard/ASU)
Our Moon may appear to shine peacefully in the night sky, but billions of years ago, it was given a facial by volcanic turmoil.
One question that has gone unanswered for decades is why there are more titanium-rich volcanic rocks, such as ilmenite, on the near side as opposed to the far side. Now a team of researchers at Arizona Lunar and Planetary Laboratory are proposing a possible explanation for that.
The lunar surface was once flooded by a bubbling magma ocean, and after the magma ocean had hardened, there was an enormous impact on the far side. Heat from this impact spread to the near side and made the crust unstable, causing sheets of heavier and denser minerals on the surface to gradually sink deep into the mantle. These melted again and were belched out by volcanoes. Lava from these eruptions (more of which happened on the near side) ended up in what are now titanium-rich flows of volcanic rock. In other words, the Moon’s old face vanished, only to resurface.